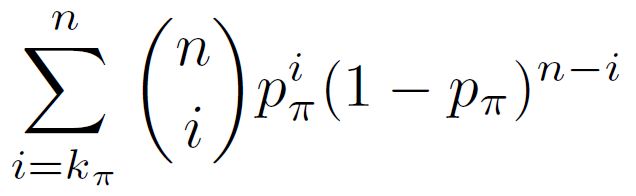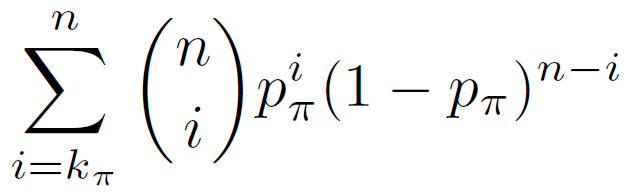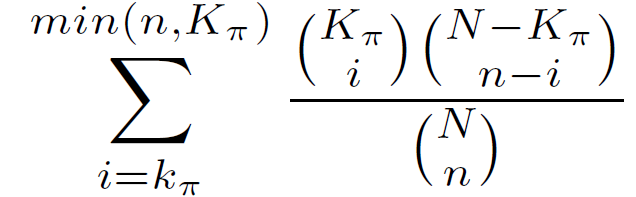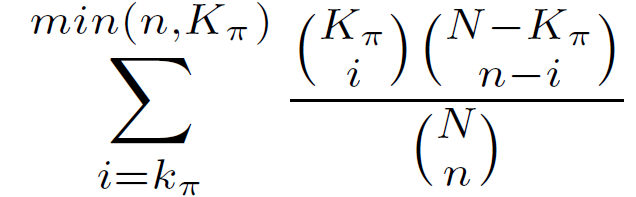...
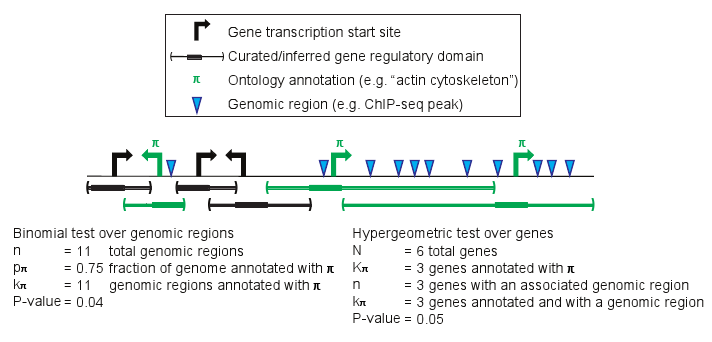
The binomial p-value equals the probability of having k? or more of the n test genomic regions in the regulatory domain of a gene with annotation ? given that the probability of that occurring for a single genomic region is p?.
Binomial P-value =
What is the hypergeometric test formally?
...
The hypergeometric p-value equals the probability of choosing k? or more genes with annotation ? when randomly drawing n genes from the genome.
Hypergeometric P-value =
Example
Explicit Background Set
If you provide an explicit background set, GREAT uses a different statistical test than for a whole genome background, a foreground/background hypergeometric test over genomic regions. Unlike the similarly-named hypergeometric test over genes used with a whole genome background, it is not biased by the differing sizes of the regulatory domains of genes.
What is the foreground/background
...
test formally?
The foreground/background hypergeometric test is a statistical test calculated for a set of genomic regions. It specifies whether a foreground (test) set of genomic regions is enriched for any annotations out of the full set of background genomic regions. The foreground genomic regions are specified in the test set, and the background genomic regions are specified in the background set. All foreground regions must be present in the background set. Formally:
...
The hypergeometric statistic equals the probability of choosing k? or more genomic regions with annotation ? when randomly drawing n genomic regions from the background set.
Hypergeometric P-value =
How should I interpret the statistics provided by GREAT? Which test is more important - the binomial or the hypergeometric?
...